Learning how to give constructive feedback on writing is a valuable communication skill. Understanding the difference between helpful and unhelpful feedback is wisdom you can apply in other areas of life – in relationships; when a friend asks your honest opinion. Learn how to give sensitive, useful critique (plus strategies for taking feedback on your own writing better):
How to give constructive feedback:
- Remember the purpose of writing feedback
- Understand helpful vs not helpful feedback
- Prioritize your suggestions
- Use the ‘slug sandwich’ to temper criticism
- Match critique style to the writer’s level
- Critique the writing, not the author
Remember the purpose of writing feedback
Why give writing feedback to others in a writing group, in a critique circle, or become a beta reader? Giving feedback:
- Helps others improve their writing so they can reach their goals.
- Improves your own problem-solving (developing critical thinking skills you can apply to your own work).
- Builds rapport with writers that sustains productive collaboration (when given in a tactful and supportive way).
The purpose of writing feedback depends, of course, on its context.
In a classroom, feedback is to assist language learners in developing skills such as composition, clarity, style and general language usage. Feedback helps you see the common language or formal errors you make most often, and learn how to avoid making the same mistakes repeatedly.
In a fiction writing group or editing process, feedback provides uses such as having an external sounding board, collaboration, and developing your writing towards a further goal (such as publication).
Understand helpful vs not helpful feedback
Helpful feedback is commentary that helps a writer to make a text a better version of itself.
It does not tell the recipient ‘you are bad’ or ‘I am better’. Rather, it is driven by an ethos of ‘let’s make this stronger, together’.
Helpful writing critique tends to provide:
- Comments aligned to the writer’s stated or implicit goals (e.g. if the author is writing romance, an implicit goal is that the story’s central conflicts involves romantic relationships, the conventions of this genre)
- Specific, actionable suggestions (compare ‘this part might be even more interesting if you…’ to ‘this part is boring’)
- Examples – compare ‘Ugh this is full of comma splices’ to ‘you have a comma splice between [two given words]’. The second pinpoints an actionable improvement
Types of unhelpful writing feedback include feedback that uses:
- Mean/unkind tone likely to discourage (e.g. ‘You should give up writing’)
- Sweeping suggestions that lack specificity (e.g. ‘This isn’t interesting’)
- Subjective bias presented as a universal value (e.g. giving a negative critique because the feedback giver does not like the genre, regardless of the writing’s own qualities)
Here is an example of less constructive feedback from the comments section of this article:
This is unhelpful propaganda. Brutal honesty is a kindness.
Commentator, ‘Irefuse’
The comment checks all three of the above points:
- Its tone is direct but unkind and discouraging in its use of negative exaggeration (accusation of a defamatory nature – the false accusation of creating ‘propaganda’).
- It makes sweeping claims without examples to back up the argument or further specificity (‘propaganda’ is defined as ‘information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote a political cause or point of view’).
- It makes the universal yet subjective statement that ‘brutal honesty is a kindness’. The truth is many writers will not experience your brutal honesty in writing groups or reviews as kind. This is where the distinction between a nuanced critique and vitriol matters, the sensitive and empathic versus the excoriating hatchet job. Empathy and intent make a difference in whether people can hear – and act on – feedback.
Critique empowers, or opens up another perspective. Criticism is harsher, the kind of ‘brutal honesty’ that may be unhelpful or counter-productive.
Let’s look at how to give good feedback on writing, given the above:
Prioritize your suggestions
A great strategy for giving critique is to prioritize your suggestions.
George Mason University has a helpful guide to giving feedback that talks about ‘Higher Order Concerns’ (issues such as overall clarity, effectiveness) and ‘Lower Order Concerns’ (minor, sentence-level issues such as SPAG, also known as spelling, punctuation and grammar).
Lead with the most important, standout aspects. First the good elements, then the areas needing improvement.
Our manuscript evaluations are structured this way (the first two sections highlighting standout positives and broad areas for improvement).
This means the writer leads with encouragement they can carry over as ‘buffer’ into any more critical observations. There’s an aura of positivity to tide them over, through any rougher patches.
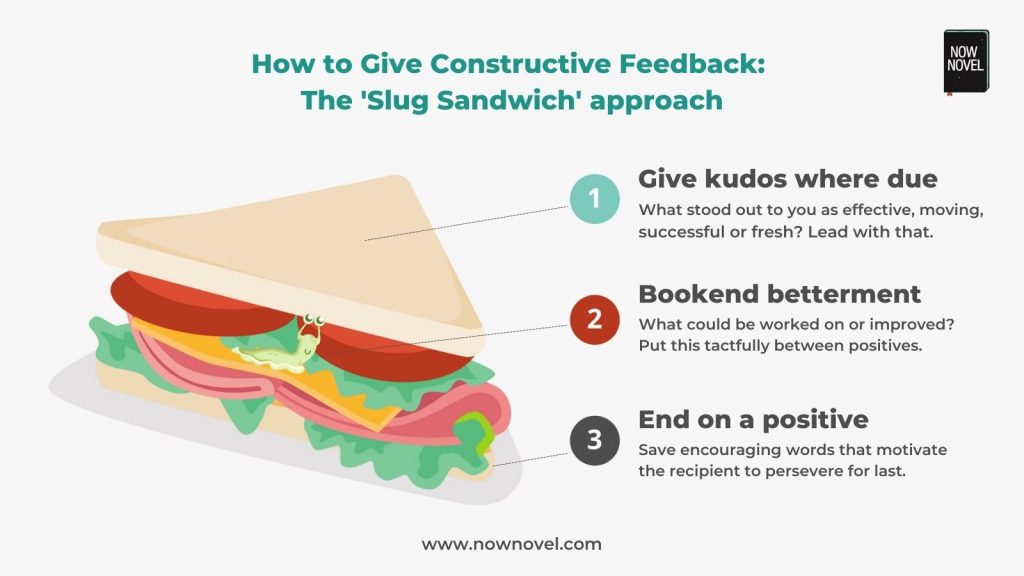
Use the ‘slug sandwich’ to temper criticism
This is a classic approach to criticism (often, a curse word replaces ‘slug’ – this is the classroom-friendly version).
What is a ‘slug sandwich’ in writing feedback? You:
- Give kudos to or acknowledge the writing’s most effective aspects – what gave you the most pleasure or appeared the most effective.
- Next, you move on to areas that (in your opinion) require further work, preferably with specific, actionable examples.
- End with sincere words of encouragement.
Example of constructive critique
An example of constructive writing feedback using this approach for the classic fable Cinderella:
[The ‘top slice’ of kudos]
Example of three-part, constructive feedback
I enjoyed how you showed the complex family dynamics between Cinderella and her step-mother and mean step-sisters – this rang true of an adjustment phase that often does happen in blended families.
[The ‘middle slug’ of suggestion]
The fairy godmother could read like a deus ex machina to some – something that comes in and saves the day, making success a little too certain or easy for Cinderella. Is there perhaps a further challenge she might have where the godmother is unable to assist her, like a ‘dark night of the soul’, something that truly tests her and she has to stand alone and ‘figure it out’ for herself?
[The ‘bottom slice’ of encouragement]
You’ve captured the relationships within the family well. Perhaps consider cutting off the godmother’s support in the rising action towards the end so that the stakes and suspense are even higher. Keep going!
Common criticisms of this feedback approach (often shared in the business world) are:
- People come away only remembering the ‘bread’ of kudos and encouragement (criticism gets lost in the mix).
- It may seem inauthentic due to having a somewhat ‘templated’ format that can seem impersonal.
These are valid objections to this approach. However, if you keep each part to the point, and strive to fill your feedback with empathy, purpose and tact (authentic connection, in other words), your feedback should still be effective.
It’s better than harsh feedback which shuts down openness and discussion.
Match critique style to the writer’s level
In a critique circle or as an editor starting out, you’ll likely find yourself critiquing writers who are writing at all different levels.
In a Critiques Live writing workshop (a Now Novel membership benefit for The Process and other plans), some Now Novel members shared that they ‘didn’t feel qualified’ to critique other writers.
This is where it’s helpful to remember that there is a difference between professional editing and peer review. Every peer has different experiences and may pick up on different elements of the story and contribute an immensely useful perspective (because of their individual field of reference).
Some writers may be ready for publication or have already published. Others might have written or have just started their first ever story.
Match your feedback to where the writer is at.
If a writer has stated, for example, that English is not their first language, cut them slack on errors of usage. Rather suggest a general grammar resource they can use for self-study if they wish than tear apart their writing error by error – unless you’ve been hired as a copy-editor for precisely this role.
The best critique helps people where they’re at, not where the reviewer thinks they ought to be. Great editing elevates, never condescends.
Critique the writing, not the author
There are times where you might read work where the characters are objectionable, or the subject matter is unsavory to you.
It is important to critique the writing rather than leap to ad hominem (personal attack).
For example, if an author writes a story where all the male characters are arrogant chauvinists and all the women are simplistic ‘bimbo’ tropes, this could be reflective of the author’s own limited awareness or sensitivity to gender issues.
They could also hold opposing views to their characters or could think they are offering excellent social critique or satire, unaware of how they could be misread.
In giving good feedback, it is thus safest to focus on the text itself. Frame criticism in terms of the writing itself. Critique the writing.
It is much more likely to reach an author if you say, for example, ‘The female characters at times seem two-dimensional, as though they only exist to satisfy the male characters’ needs, such as when…’.
Compare this to writing feedback that says, ‘Gross, you’re a sexist pig’…
Nuanced feedback opens dialogue instead of shutting down communication (when feedback giver and recipient are open to it). This allows for true improvement and learning.
How to take constructive feedback better
Giving good writing feedback is one challenge. Receiving it without it denting your motivation is another entirely.
In a recent open Now Novel writing webinar, an attendee asked in the Q&A portion how to take feedback.
You could try:
- Skim for tone. Is writing feedback given with tact, care, precision and purpose? If not, don’t give it too much weight or power over your self-belief. Don’t even read it to the end if it appears mean-spirited.
- Pretend you’re reading editorial feedback for another author. (Active dissociation can help to make it feel less personal.)
- Look for supporting statements: Does your reviewer support any suggestions or statements with examples from your own story or others?
- State the specific type of feedback you’re looking for upfront. For example, if you struggle with detailed description, you could say ‘Please suggest how I could improve my descriptions’. If feedback doesn’t fulfil your brief you then have reason to skip it.
Need constructive feedback? Get a free sample edit when you request a quote for our fiction editing services.
Further resources
Angela Ackerman offers excellent advice on how to handle critiques of your own work: Evaluating Critique Feedback.
K.M. Weiland gives succinct pointers on sorting good feedback from bad: How to Get Feedback on Your Writing (and Sort the Good from the Bad).
Although business-oriented in scope, Scott Halford’s piece for Entrepreneur raises how important it is to create an atmosphere of safety in giving feedback.
What’s the best writing advice you ever got? Tell us in the comments.




17 replies on “How to give constructive feedback on writing that rocks”
This is so timely for me, it’s uncanny. Thank you, Jordan. I had reached an impasse and almost wanted to quit my writing group. Now I see a way forward.
Hi Heather, I’m so glad to hear that. If it’s not a fit with your writing group, I would say you’re completely within rights to seek a better fit. I hope the way forward works out. Thank you for sharing your feedback.
Thank you for this. The key points for me were: a) Make a text better a better version of itself. b) Lets make this stronger, together. Be specific, use actionable suggestions, while encouraging continued writing. Perfect.
Hi Jamie, it’s a pleasure. Thank you for reading this.
Its very helpful.
Thank you for your feedback, Khuzaima. I’m glad you found this article helpful.
This is unhelpful propaganda. Brutal honesty is a kindness.
Hi ‘Irefuse’. ‘Brutal’ and ‘kindness’ are somewhat oxymorons. Calling an article about constructive critique with suggestions on ways to give it ‘propaganda’ is a STRETCH, though. I’m sorry you personally found it unhelpful, next time the constructive criticism would be suggesting ways to make it better, pinpointing the arguments or passages you took issue with and how they could be improved. I’m sure when you find the bravery to share work in the public domain you will have to deal with comments that only seek to tear down and label. Good luck when you do.
Jordan, most exalted kudos to you and your response to “Irefues”. I am not sure how anyone would or could find your article unhelpful unless they were not looking to get potentially useful information relating to critique about one’s own writings or how to give criticism to others on their writings. I will also say that your response was very professional and yet I sensed in your word usage and structure that it was meant as a zinger to illustrate very tactfully your last two statements. Brilliant. Thanks for your article and your response to those commenting on it.
Hi Michael, thank you very much. Everything from the username to the email given (which completed the phrase ‘I refuse to sign up’) had an aggressive/pointed streak which made it clear it was more of a trolling attempt to be unkind than serious critical engagement. I always say to writers it’s best to say ‘water off a duck’s back’ because trolls can be persistent, cruel, and vicious, and you don’t want a negative feedback pile-on or something more nefarious or ‘black hat’. That being said, this duck can be spicy, the water drying before it hits the ground 🙂 I try to turn rudeness/unkindness into a teachable moment (I think I bristled at the false accusation of producing ‘propaganda’ – a real nonsense), and I’m glad that came through. Thank you for reading our blog and I’m glad you found it helpful.
I am sorry but I misrepresented what I need from you. I am writing down information that is true and simply want a few adjustments made to what I wrote. It is not a novel but more of a report from one person to another.
Hi Susan, I don’t see any other communication (regarding what you said about a misrepresentation)? Perhaps you typed a comment on another article but it’s not showing for me. Are you looking for editing services (your reference to wanting adjustments made)? You can request a no-obligation editing quote via our editing services page.
This is clearly a much-needed article! I’m so glad it’s now linked in the feedback section. “Brutal honesty” means nothing in terms of improvement unless it comes with an acknowledgment of what was attempted and how to take next steps. The research is clear.
I really loved how you turned a negative comment on your own work into something that improved this article. Really good use of the examples– they helped strengthen the points about what good or bad feedback sounds like. I remember having a good friend who I shared my work with, and they dismissed it as “cheesy”. I knew they had good intentions and wanted me to improve, but the way they phrased it hurt me. This led me to question how I can share feedback to others without sounding hurtful like my friend. Thank you for this article. It helped me avoid mistakes I might have made.
Dear Mackey,
Thanks for your comments on the blog. Yes there’s a way to give feedback that is constructive and helps you improve your writing. So pleased to hear that you have found it helpful.
Good article. There is an art and craft to this. One of the first ‘feedback templates’ I was ever introduced to asked 1) What was communicated?
This question alone yields so much useful information to the writer because what they might want to say and do say are vastly divergent.
That’s an excellent question to ask about a piece of writing, Scott. Thanks so much for sharing it. And thanks for reading the blog.